Difference between revisions of "Eco-score transport - en"
| Line 114: | Line 114: | ||
==== Centroid worksheet ==== | ==== Centroid worksheet ==== | ||
| − | The centroid sheet lists the centroid for each country in the world. With OSM the closest town has been identified. In order to be able to calculate distances by road through OpenStreetMap, we need identify the closest town to this centroid. | + | The centroid sheet lists the centroid for each country in the world. With OSM the closest town has been identified. In order to be able to calculate distances by road through OpenStreetMap, we need identify the closest town to this centroid. (Be careful with the place name recognition in OSM, sometimes the wrong location is given.) |
| − | The centroids were taken from [http://worldmap.harvard.edu/data/geonode:country_centroids_az8 here]. The countries in this list have been used as a starting point. | + | The centroids were taken from [http://worldmap.harvard.edu/data/geonode:country_centroids_az8 here]. The countries in this list have been used as a starting point. Some centroids have been recalculated based on largest cities and population sizes. |
The worksheet contains the following rows and columns. | The worksheet contains the following rows and columns. | ||
Revision as of 10:44, 31 January 2021
Introduction
In January 2021 the eco-score has been launched. The eco-score is a label that indicates the environmental impact of a product. It is based on the lifecycle of ingredients in a product and their relative impact. This impact has been assessed for the agricultural methods used in France.
Although the eco-score is based on France, OFF would like to extend the eco-score to other countries. This involves adding the country specific aspects for:
- labels
- packaging
- logistics
In this document the logistic aspects are investigated.
Approach
The eco-score calculation adds a correction to the base Agribalyse data in order to correct for additional transport. This should correction should favor products, which are produced near to the consumer.
There are two transport corrections that can be taken into account:
- ingredient transport - transport of individual ingredients to the production location. Is this already accounted for in Agribalyse? Can it be finetuned?
- product transport - the impact of transport between production location and consumption location.
Caveat
Before diving into all kind of modelling, we must ask ourselves whether it is worthwhile. We might add all kind of complexities, which have no influence on the end result.
The base Agribalyse data probably have an error of 10% or more, as it is the result of averaging and combining all kinds of data. So if we correct for a transportation impact, it is of no use to add details better than that 10%. We will evaluate this when we start the calculations.
Transport modes
Pour les pays européens, le score est pondéré en fonction du mode de transport utilisé entre le pays d'origine et la France.
Pour les pays en dehors de l'Europe, le mix modal considéré est 100% maritime.
Goods can be transported via road, rail or waterways. The transport modes are described in Eurostat report (2009).
The goods we are interested in (related to food) fall in the following NST/R categories (table 4.6, p66):
- 0/1 - cereals;
- 0/2 - potatoes, other fresh/frozen fruits and vegetables;
- 1/6 - foodstuffs and animal fodder;
- 1/7 - oil seeds and oleaginous fruits and fats;
We assume that Agribalyse takes care of the environmental impact in producing consumer ready products. This implies we are not interested in the transport of bulk raw products.
NST/R category 1/6 will be the most important category. For this category the most important transport mode is the route (table 4.7, p67).
Transport routes
La distance entre le pays d'origine et le pays de destination est calculée à partir du centre géographique du pays de départ et celui de la France.
Pour chaque itinéraire ferroviaire ou maritime, 2 trajets en camion sont pris en compte : l'un dans le pays d'origine entre son centre géographique et son lieu d'embarquement le plus proche, l'autre en France entre son lieu de débarquement le plus proche et le centre de la France
We should look at the environmental impact for transporting goods between the production location and the consumption location. If both locations are known we can use the road distance between the two locations to get a good indication.
If these locations are not known, we need to use an estimation based on the information that we do have. The more unformation we have, the better the estimate will be.
No info
Without any additional info, there is not much to estimate. We know that it will be on average half the circumference of the world and probably much less. And this will also imply that the product is transported by sea and/or air. And assume that the product is transported to the Centroid of the country.
Purchase country
If we know the country where the product was bought, we can make two assumptions:
- product is also produced in the country;
- product will be consumed in the purchase country;
We can then take an average transportation route of half the size of the country. This will also imply a route by road.
Production country
If in addition to the purchase country, we also know the production country, we can determine the route between both countries. This might involve transport by road, air or sea. Which transport means is used will also depend on the product category.
As we do not know the exact location of production or consumption, we need to use the geographic center of a country as an approximation.
Actual Locations
If either the purchase (consumption) or production locations are known, we can perform a more detailed calculation based on the the two locations and/or geographical centers. Such a calculation will be a low estimate, as we do not take into account the actual distribution network (distribution centres, transport network, purchase places).
Score
Le score transport est intégré au score global du produit sous la forme d'un bonus allant jusqu'à 15 points.
The CO2 impact must be translated to a score from 0 - 100. A score of 100 represents the country in question, i.e. the product did not cross a border. Any other country should be less than 100. A score of 0 represents the worst case, i.e. the largest impact. These scores must be calculated for each origin. These scores will be applied as bonus, so it is assumed that the ACV of the product is the worst case.
The steps involved are:
- Max-impact - we need a good estimate for the maximum CO2 impact. You would expect that getting something from an island in the Pacific (20.000km away) would have the most impact, but is better than transporting something from Greece to France by truck. We set the maximum impact at the largest distance by maritime mode. This might punish road transport as well. This value will be used to normalise all other impacts. In practice this implies that only the islands in the Pacific will have a score of 0.
- Transportation Mode impact - when we do not know the mix of transportation modes used between countries, we will assume that the worst mode has been used, i.e. the mode with the worst impact.
Non-mixed score
The formula for the score of an origin for a country is:
scoreorigin(country) = 100 - max(impactorigin(maritime), impactorigin(road)) / maxall origin(impact(maritime))*100.
with
- impactorigin(maritime) - the impact for origin for the maritime transportation mode
- impactorigin(road) - the impact for origin for the road transportation mode
- max(impactorigin(maritime), impactorigin(road)) - the maximum impact of the two transportation modes for the origin.
- maxall origin(impact(maritime)) - the maximum impact of all maritime origins
Mixed logistics
If we have the transportation mix this becomes:
scoreorigin(country) = 100 - summode=0N fractionorigin(mode) impactorigin(mode) / maxall origin(impact(maritime))*100.
with
- impactorigin(mode) - the impact for origin for the transportation mode
- fractionorigin(mode) - the fractional impact for origin for the transportation mode [percentage]
- max(impactorigin(maritime), impactorigin(road)) - the maximum impact of the two transportation modes for the origin.
- maxall origin(impact(maritime)) - the maximum impact of all maritime origins
Country correction
And finally we need to apply a country correction. The lifecycle data is based on France, and especially on the size of France. Any logistics impact should correct for this, i.e. subtract the impact for France and add the impact for a country.
To do this the mean transportation distance for a country will be estimated and the corresponding environmental impact. The impact for France will be subtracted and the impact for the country added. The mean transportation distance is half of the largest distance that can be travelled in a country.
The non-mix formula becomes:
score(origin, destination) = 100 - (max(impactmaritime(origin,destination), impactroad(origin,destination)) - (impactroad(mean France) - impactroad(mean destination)) / maxall origins(impactmaritime(origin,destination)*100
The consequence of this country correction is that locally produced (in the country) products, may have a higher score than 100. It just reflects that smaller countries have an advantage over France.
As the score is normalised by the maximum impact, any country correction is not seen in the score.
Calculation method
The entire calculation method for the logistics impact is put into a spreadsheet: here. The details of each worksheet of this spreadsheet will be explained below. This spreadsheet format should allow to make changes easier and see the impact of these changes.
The spreadsheet is setup is such a way, that the environmental impact of logistics can be calculated for any territory or country in the world.
Centroid worksheet
The centroid sheet lists the centroid for each country in the world. With OSM the closest town has been identified. In order to be able to calculate distances by road through OpenStreetMap, we need identify the closest town to this centroid. (Be careful with the place name recognition in OSM, sometimes the wrong location is given.)
The centroids were taken from here. The countries in this list have been used as a starting point. Some centroids have been recalculated based on largest cities and population sizes.
The worksheet contains the following rows and columns.
- rows The rows represent areas for the origin or destination using a specific port of entry into that area. An area can be a country or part of the country. A part of the country can be anything that makes sense and refines the logistics impact.
All these rows should repeated on other spreadsheets both as rows and as columns.
- columns
- area name: the name of the country or smaller area, such as a specific island;
- centroid: the latitude and longitude of the (geographic) centroid;
- centroid name: the geographic name that corresponds to the centroid, according to Open Street Map;
- sea port: the name of the main container sea port (as a link to the sea ports worksheet). The sea port does not have to lie inside the area (land-locked countries);
- sea covered: the sea covered by the port. An area can have multiple sea ports, one for each sea covered (Pacific/Atlantic for the UAS, Atlantic/Mediterranean for France, etc.);
- distance: the distance (in km) between the sea port and the centroid of the area;
- OSM-link: the link to the directions on Open Street Map, from which the distance was taken.
Container port worksheet
For each of the area's on the Centroid-worksheet a row and a column is created in the Container port worksheet. In addition two columns that document a port have been added: one column is a link the wikipedia-page of the port and one column is a link to the port authority of the port.
Each cell that links to ports shows the maritime distance between the two ports, as calculated by Searates.
Maritime Route matrix worksheet
This worksheet contains the links between all countries that have been listed on the first worksheet. Each cell describes the environmental impact of maritime transport between two countries. The environmental impact is calculated by the route between origin and destination centroid, via the closest seaport. From and to the seaport the road cost is used. The maritime cost depends on the route taken by the boats. We distinguish multiple routes:
| Transportation mode | Impact |
|---|---|
| Road | Example |
| Coasters | |
| Across the atlantic | Example |
| Via suez canal | Example |
Road Route matrix worksheet
This worksheet contains the impact of transportation between the countries by road. Each cell contains the impact between two countries. The distances are based on the centroids of the countries, and the distances of the directions calculated by OpenStreetMap. Routes that contain a trip by sea are taken from Google Maps.
Each distance is multiplied by the environmental impact per km.
The route distances are calculated up to a distance of 2000 km. If the distance is larger than that, a route by sea is preferred (and has less impact). This is an arbitrary number for the moment.
Score matrix worksheet
The score matrix contains the (bonus) scores based on the two route worksheets. If a route is available by road and by sea, the road one is preferred and used in the calculation.
The impact is normalised in order to calculate the score.
Intra country logistics
Does the eco-score or ACV take into account the impact of logistics required within a country? This probably needs to be changed for countries with different sizes. Not sure what is the best way to calculate the mean distance for each country.
A worksheet is reserved for the recording of the mean size and the environmental impact.
Check
the calculations and spreadsheet described above should be checked against the values publish by Eco-score. This can be achieved by recalculating the values for France.
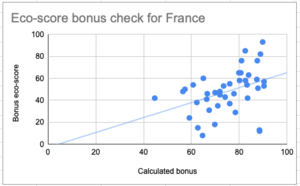
The first take at the calculations can be seen in the graph below:
From the graph it can be seen there is still work to be done:
- The eco-score values are in general lower than my calculation. This can be due to a different normalisation: what should be used as maximum, that corresponds to eco-score value 0. I used the impact to islands in the Pacific;
- Is there a cutoff distance, where we rather transport by boat than road;
- I did not use any modal mix and assumed the worst option by road;
- There might be centroid issues, for instance why has Monaco (south of France) a worse eco-score than Denmark? Would also imply that internal transport should be taken into account.
- There are many large individual differences reflecting other choices that have been made in centroids, distances, impact, etc. We really need to be more transparency and thus might get more consistency.
Thoughts
The calculation method used by Eco-score to assess and add the environmental impact of logistics to the base Agribalyse score is still in its infancy. Undoubtedly it will be improved and extended in the future. I list some thoughts here, where I see issues.
Base calculation method
The calculation method used for the Agribalyse normalisation and bonus/malus system makes it difficult to understand. Ideally the Agribalyse CO values and the transport malus are comparable. This is not the case at the moment. So what does a transport malus actually mean? I would prefer a method where the normalisation is done after applying all the bonus/malus. So that in effect the Agribalyse values are directly adapted by the bonus/malus application.
Transparancy
In order to extend the transport malus to other countries, I needed to know the actual calculation methods. These are not yet public. I hope everything will be be public and in the oublic domain.
Extendability
The eco-score calculation should be extendable. A public procedure should be setup, which allows to do this. This procedue could be similar to what is used in open software projects.
Reversal of evidence
The current calculation method makes a lot of assumptions about labels, logistics, etc. Ideally it should not be eco-score that makes the assumptions, but the producers that provide the data. This should reduce any greewashing allegations.
Country centroids
The centroids used for countries can be improved in several ways:
- population centroids - instead of the geographic centroids we need a center based on the population distribution, so that we can take better into account where the goods will flow (link). This is especially useful for countries we geographically unevenly distributed populations.
- very large countries (Australia, Canada, Chili) - the geographic centroids cover an area which is just to large, we need to look at the territories within the country seperately. This is also true for France if the DOM's are taken into account;
Maritime container seaports
For each country the most appropriate container port must be identified. The following issues complicate things:
- Some countries have multiple ports. Are different ports used for different origins?
- Landlocked countries (Burundi, Switzerland, Bhutan): where do they get their maritime goods from and how? We need to look at each country individually;
Optimally we need a local logistics expert for each country, which can fill in the details. We can offer the hooks so that in the future better values can be easily incorporated.
Logistics modal mix
Many assumptions need to be made on the modal mix. Without any additional info we only assume road and sea. Sometimes a product gives an indication of the modal mix, by saying it has been flown in. But clearly more transparancy is needed.
Logistics environmental impact
For the environmental impact of logistics we now narrowly look at CO2. We should also look at all other effects of logistics, i.e. other pollutants, impact on space, vehicles, etc.
Intra-country logistics
The lifecycle and the eco-score corrections are based on averages for each country. It would be even better to take into account the positive effects of buying really locally produced products. This can be achieved if additional information on producer and buyer is taken into account. Instead of the average assumptions for a country, the actual distance between producer and buyer can be used. (This does not take into account the distribution chain of a large supermarket chain)
In order to achieve this we can adapt the country correction:
- always (also in France) subtract the mean distance (and impact) for France
- calculate the distance between producer and buyer. This can be based on the producer code and the purchase location. OSM might be used for this calculation.
- calculate the environmental impact
- calculate the more exact score
Bonus or malus?
Why is the score defined as a bonus? The lifecycle analysis of a product is based on the logistics impact of transport in France. A bonus would be logic if a product is sourced even more locally, i.e. in the geographic neighbourhood of the purchase location. If you use a product produced outside France it should imply a malus.
Thus a bonus of 0, should imply no distance larger than the mean distance, a larger distance would imply a malus and less distance a bonus.