Country correction
This page explores how the size of the country can be taken into account in the determination of the eco-score transport bonus.
Bonus approach
The eco-score approach intends to give a bonus to locally produced (and purchased) products. This bonus is +15, which is equal to a transport score of 100. This bonus is however now given to any product produced/purchased in France. No account has been taken of the very large size of France and impact of transport within the country.
Can this approach be adapted, so that the size of a country is taken into account?
Maximum bonus
It would be logic to give the maximum bonus (transport score if 100) only to very locally production and purchase. Ideally this will imply an area as small as possible, i.e. a city or very small country. Production and purchase that occurs in a country such as Andorra, Monaco, Liechtenstein or San Marino could be viewed as having a transportation score of 100.
No bonus
In the current calculation the no bonus (transportation score 0) is (arbitrarily) set at a distance of 2000 km. This distance covers roughly the size of Europe.
Centroids to the rescue
Is it possible to use the centroid calculations in determining the (transportation) size of a country?
The weighted sum for a country that consists of single city will be zero. This can then correspond to a transportation (bonus) score of 100. This means it is preferred to have no transportation.
The weighted sum of the major cities in the European Union (or larger area) could be used to define the transportation score of 0. This means a maximum transportation impact.
From Any weighted sum in between it is now possible to calculate a country transportation score. The larger the country, the lower the country transportation score. This country transportation score can be used to determine the maximum bonus for a country.
The centroid approach can also be used to calculate the country transportation size. We just have to add all cities, so that the entire population is covered. The resulting weighted distance is the size we are looking for.
In practice this approach is not feasible. It is just to much work to (to do by hand a least). So we need a way to get a reasonable approximation. For the calculation of the centroids a limited number of cities are used. We could try to extrapolate this data to get the transportation country size.
Approach
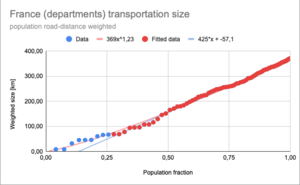
In the figure the results for the french departments are shown.
The cumulative population road-distance weighted distances are plotted against the cumulative population ratios. Each added city adds a point, increasing the cumulative population ratio and the cumulative distance. If the cumulative population ratio is 1, we have covered the entire population. And the corresponding cumulative distance is the value we are looking for.
Adding all the cities is to much work. Instead of adding all the cities, we could fit a line to the data of a few city points. The cumulative distance of the fit at a population ratio of 1, is then again the value we are looking for.
The function to fit must behave nicely with extrapolations. This excludes complex functions with many parameters. Or functions which behave not regular outside the fitted points (polynomials).
This leaves the following functions in Google Sheets:
- linear - results in average values;
- logarithmic - results in smaller values;
- power functions - results in larger values, but goes through (0,0);
The results of France show that the logarithmic function does not fit the data. The best fit is provided by a power functions. However this works only if there is enough data above a population fraction of 25%. The data below 25% heavily influences the outcome of a power functions. As an approximation a linear fit, without using the data at low values gives a better estimate. For France in fact the results are the same.
Result
This approach has been applied on the following countries with a power function:
| Country | Centroid city | size | spreadsheet |
|---|---|---|---|
| Albania | Tirana | 100 | link |
| Algeria | Algers | 370 | link |
| Austria | Vienna | 230 | link |
| Belgium | Brussels | 86 | link |
| Bosnia and Herzegovina | Zenica | link | |
| Croatia | Zagreb | 160 | link |
| Czech Republic | Prague | link | |
| Denmark | Copenhagen | 170 | link |
| Estonia | Tallinn | 120 | link |
| Finland | Helsinki | 220 | link |
| France - cities | Paris | link | |
| France - departments | Paris | 369 | link |
| Germany | Hannover | 260 | link |
| Greece | Athens | link | |
| Hungary | Budapest | 120 | link |
| Iceland | Reykjavik | 90 | link |
| Ireland | Dublin | 100 | link |
| Italy | Rome | 520 | link |
| Latvia | Riga | 77 | link |
| Lithuania | Kaunas | 120 | link |
| Montenegro | Bijelo Polje | link | |
| Morocco | Temara | 230 | link |
| Netherlands | Utrecht | 72 | link |
| Norway | Skien | 300 | link |
| Poland | Łódź | 240 | link |
| Portugal | Lisboa | 140 | link |
| Romania | Bucharest | 300 | link |
| Slovakia | Banská Bystrica | 78 | link |
| Slovenia | Ljubljana | 66 | link |
| Spain | Madrid | 430 | link |
| Sweden | Nörrköping | 270 | link |
| Switzerland | Olten | 120 | link |
| Tunisia | Tunis | link | |
| United Kingdom | Coventry | 210 | link |
| European Union | Munich | link | |
| Bouches du Rhône | Marseille | 22 | link |
Values in italic need more data.
Comments
Some observations on individual countries.
Conclusion
The graph below shows the size of each country based on population road-distance weighted transportation distance. The location of the circles is on the country centroid.
So what to do with this data? The idea is to extend the ecoscore to other countries. A consistent approach should allow comparison between countries and favorise local production and consumption.
How the transportation is incorporated depends on what the ecoscore wants achieve. There seem to be three approaches.
Real approach
Bonus approach
Ecoscore approach
The ecoscore is developed for France and favorises products from France. To achieve this a bonus is given to any product